Heroin is a highly addictive and illegal Schedule I controlled substance.[1] The drug contains a mixture of diacetylmorphine, the active ingredient that produces opioid-like effects, and a number of fillers and additives. In general, there are four different types of heroin:
- Black tar heroin
- Brown powder heroin
- White powder heroin
- Purple or blue heroin
While each type produces similar effects, they are all different in appearance, texture, and composition.
Psychoactive Ingredients in All Types of Heroin
The primary psychoactive ingredient in heroin is diacetylmorphine, also known as diamorphine. It is a highly potent opioid painkiller that is derived from the sap of the seed pod of opium poppy plants. These plants are native to Southwest Asia, some areas of the Middle East, and Mexico.
Diacetylmorphine is the ingredient that is responsible for the euphoric, pain-relieving effects produced by heroin. It is also responsible for heroin’s addictive and habit-forming characteristics.
Once in the body, diacetylmorphine is metabolized into morphine, a potent opioid painkiller.
While heroin is technically diacetylmorphine, the heroin people purchase on the street may contain a number of additional psychoactive ingredients, such as:
- Fentanyl – a synthetic opioid painkiller that is 50-100 times stronger than heroin and morphine.[2]
- Carfentanil – a synthetic opioid that is used as a horse tranquilizer and is 100 times stronger than fentanyl.[3]
- Methamphetamine – a powerful stimulant drug that produces feelings of euphoria.
- Prescription drugs – usually opioid painkillers like OxyContin or benzodiazepines like Xanax.
Understanding the Different Types of Heroin
Heroin may appear in four or more different forms, including:
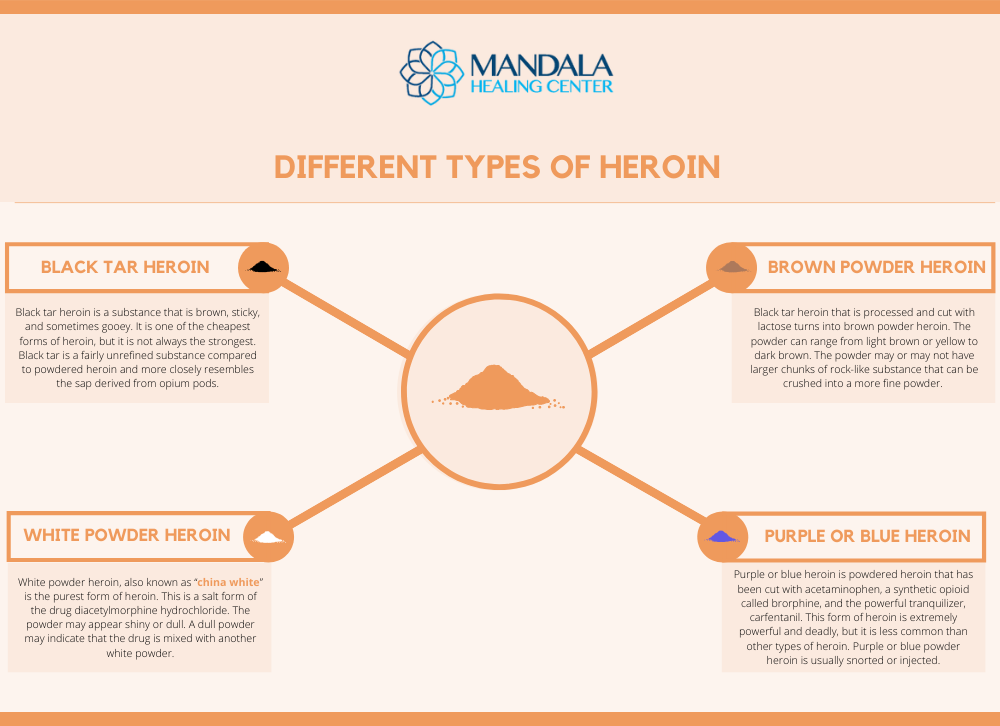
Black Tar Heroin
Black tar heroin is a substance that is brown, sticky, and sometimes gooey. It is one of the cheapest forms of heroin, but it is not always the strongest. Black tar is a fairly unrefined substance compared to powdered heroin and more closely resembles the sap derived from opium pods.[4]
Black tar heroin is too sticky to be snorted, so users usually dissolve and inject it or smoke it on aluminum foil.
Brown Powder Heroin
Black tar heroin that is processed and cut with lactose turns into brown powder heroin. The powder can range from light brown or yellow to dark brown. The powder may or may not have larger chunks of rock-like substance that can be crushed into a more fine powder. Brown powder heroin is usually produced in Mexico and distributed in the United States.
This type of heroin will only dissolve when heated, so it is usually snorted, smoked, or injected.
White Powder Heroin or “China White”
White powder heroin, also known as “china white” is the purest form of heroin. This is a salt form of the drug diacetylmorphine hydrochloride. The powder may appear shiny or dull. A dull powder may indicate that the drug is mixed with another white powder.
White powder heroin may also appear off-white, beige, or even pink depending on its extraction and processing methods. People often inject this form of heroin.
Purple or Blue Powder Heroin
Purple or blue heroin is powdered heroin that has been cut with acetaminophen, a synthetic opioid called brorphine, and the powerful tranquilizer, carfentanil. This form of heroin is extremely powerful and deadly, but it is less common than other types of heroin. Purple or blue powder heroin is usually snorted or injected.[5]
Other Heroin Combinations
Sometimes, heroin is intentionally mixed with other substances to produce certain effects. Other types of heroin include:
- Cheese heroin – a mixture of black tar heroin and cold medicine that has the appearance of a light brown powder
- Gunpowder heroin – a particularly strong version of black tar heroin
- Scramble – a capsule containing heroin and benzodiazepines
Additives, Fillers, and Toxins Found in Street Heroin
How heroin is made varies greatly from one illicit drug manufacturer to the next. Even when obtaining heroin from the same dealer, there can be a lot of differences between batches.
Dealers often use fillers to bulk up their substance and increase their profits. Some substances that are used as fillers in heroin include:
- Talc powder
- Flour
- Cornstarch
- Sugars
- Powdered milk
- Quinine
They may also cut heroin with a number of additives that increase the effects, such as prescription drugs, local anesthetics like xylocaine, and synthetic opioids.
Since heroin is an illegal drug, it is usually manufactured in clandestine laboratories by unqualified individuals. This can result in accidents, contamination, and the potential for deadly toxins to enter the drug supply. As a result, all types of heroin may contain chemical additives and toxins such as:
- Ammonia
- Chloroform
- Hydrochloric acid
- Acetic anhydride
Black tar heroin may contain harmful contaminants like:
- Strychnine (rat poison)
- Clostridium botulinum (a toxic spore that can cause botulism)
Find Help for Heroin Abuse and Addiction Today
Regardless of the form of heroin that is used, the drug is highly addictive and deadly. In recent years, deaths involving fentanyl and heroin have increased dramatically.[6] Consuming any kind of heroin is a gamble with life and death. Although stopping heroin can be challenging, it is possible with the help of a holistic opioid treatment program.
If you or a loved one are addicted to heroin, there is no better time to get help. Our team at Mandala Healing Center can assess your individual needs and help you choose the right treatment plan for you. Don’t wait any longer. Start your recovery journey today.
References:
- https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/drug-scheduling
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/fentanyl/
- https://www.justice.gov/usao-edky/file/898991/download
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5027195/
- https://www.phsd.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/CDS_Drug_Alert_Carfentanil-wih-Heroin_Mar_29_2018.pdf
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/heroin/scope-heroin-use-in-united-states